Single phase induction motors
A single phase induction motors is a type of single phase motor.
Constitution or parts
A single phase induction motor is made up of two main parts. Namely: the stator and the rotor and may include other accessories like centrifugal switch etc, capacitors.
 |
| Internal view of a type of single phase induction motor with view of a centrifugal switch and capacitor |
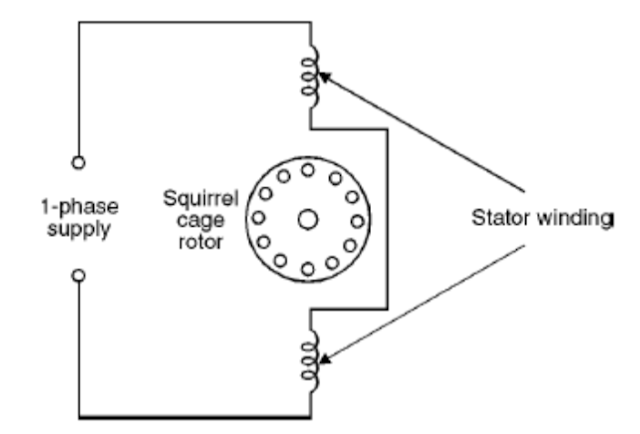
Stator: The stator carries single phase windings (main winding and start winding for starting). These windings are distributed ( uniform or equal distribution of the conductors in the slots).
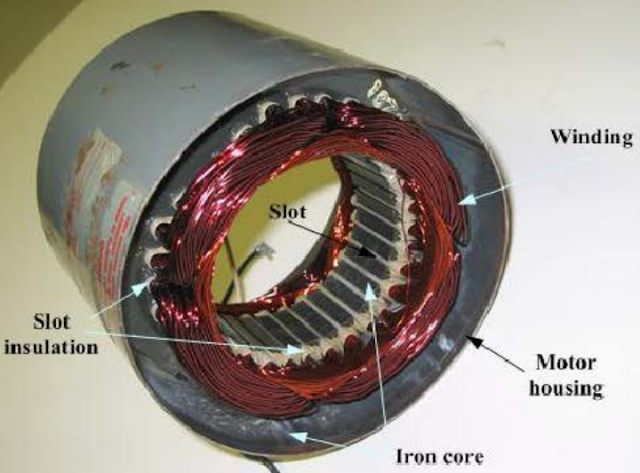 |
| Stator of a single phase induction motor |
Rotor: The rotor of a single phase induction motor is of squirrel cage type (Squirrel Cage rotor)
A centrifugal switch may also be incorporate into the motor ( connected in series with the starting winding) and is used to cut off the starting winding when the rotor accelerates to about 75% of the rated speed.
This switch is usually mounted on the rotor's shaft.
This switch is usually mounted on the rotor's shaft.
Representation
Let's see how we can represent the rotor and the stator.
Operating principle of single phase induction motors
Supplying the stator with single phase supply, causes current to flow through the stator conductor which creates an alternating magnetic field (flux) around it. This flux is induced into the rotor and therefore, current flows in the rotor conductors and also produces a magnetic field. Despite the production of these two fields, the rotor does not rotate. This is because the magnetic field produced does not rotate but alternates. Consequently, a null (zero) resultant torque is produced which can not rotate rotor but only vibrates. So, a rotating magnetic field is necessary to produce a torque to rotate the rotor. That is why single phase induction motor are not self starting.
So, in order to start this motor, a rotating magnetic field needs to be created. This can be achieved by introducing a starting winding, which permits a 90 degrees phase shift to be created between the current in main winding and that in starting winding.
Types of single phase induction motors (Starting methods)
The types of single phase induction motors are named based on their starting methods. They are:
- Split – phase Induction Motor
- Capacitor – Start Motor
- Permanent – Split Capacitor Motor
- Capacitor - Start Capacitor - Run
- Shaded Pole Induction Motor