How a Hydroelectric power Station Works
A hydroelectric power plant is a power station which produces electrical energy from the energy stored in water at certain heights, with the use of a turbine which is mechanically coupled to a generator.
So water is the primary source of energy in this type of power plant.
In order to understand the conversion process, we shall chronologically study the different components and their role in the conversion process. The diagram below is a schematic diagram of a hydroelectric power plant.
So water is the primary source of energy in this type of power plant.
In order to understand the conversion process, we shall chronologically study the different components and their role in the conversion process. The diagram below is a schematic diagram of a hydroelectric power plant.
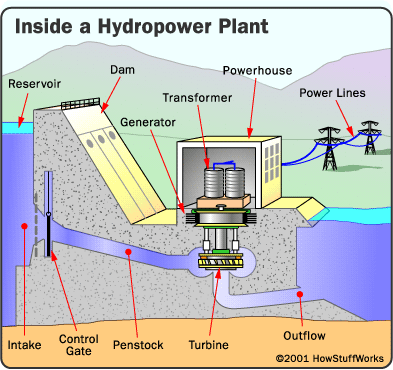 |
| Layout of a hydroelectric power plant |
The
essential components of a hydroelectric power plant as seen in the diagram
above include:
- Reservoir: it is used to maintain the water reserved.
- Dam: holds back water in the reservoir. It is important to note that, the water is held at a certain height. So, this water has potential energy.
- Penstock: this is the passage which channels the water into the turbine. As the water runs down the penstock into the turbine, part of the potential energy is being converted into kinetic energy (running water has kinetic energy).
- Turbine (water turbine): this is a rotating mechanical structure designed to rotate freely when water flows through it. As the water passes through the turbine this rotates the turbine. Hence, the energy is being converted into mechanical energy (rotational motion).
- Generator: it is used to convert the mechanical energy produced by the turbine into electrical energy. So, a generator is mechanically coupled to a turbine which provides the rotating mechanical force to rotate the rotor of the generator in order to produce electrical energy.
- Transformer: step-up transformers are usually used to step up the voltage at same frequency before being transmitted.
- Gate control: used to control the amount of water intake into the penstock to the turbine.
- Tail race (out flow): this is the water outlet from the turbines outlet into the river.
Advantages of a hydroelectric power plant
- Used for bulk energy production because primary source is usually readily available. Hence can be used for peak and base loads depending on the period.
- Running this plant is less costly because primary source of energy ( water) is free.
- Considered as a green source of energy since water is readily available in nature.
- Hence Pollution free.
- Easy control and maintenance.
- Water in the reservoir could be used for other purpose e.g fish pond, etc.
Disadvantages of a hydroelectric power plant
- Seasonal changes such as dry seasons may cause a decrease in water level. So this requires accurate planning for water storage in the reservoir (water reserve).
- The reservoir may serve as a breathing ground for mosquitoes.
- If the dam and reservoir is not properly handled. Water may cause flood
- Requires large surface area.
- High initial investment but less costly to run when already installed.